Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It leads to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells, which can disrupt the body’s ability to fight infections. There are several types of leukemia, including Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Each type has unique characteristics and treatment methods. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. In this article, we will explore 10 essential facts about leukemia, including its symptoms, types, and treatment options.
Fact 1: Leukemia Originates in the Bone Marrow
Leukemia starts in the bone marrow, the soft tissue inside bones that produces blood cells. This cancer leads to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells, which can interfere with the body’s ability to function properly. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) states that leukemia affects both the blood and bone marrow, causing various symptoms that can impact a patient’s health.
There are different types of leukemia, such as Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML), and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Each type has distinct features and treatment approaches. For example, AML is the most common acute leukemia in adults and can lead to serious health issues if not treated promptly. Symptoms often include fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and unexplained weight loss, making early diagnosis essential for effective treatment (Leukemia Care).
Recent advancements in leukemia research have improved treatment options. Traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation are now complemented by targeted therapies and immunotherapies. For instance, CAR T-cell therapy has shown promise in treating ALL, especially in children and young adults (Advances in Leukemia Research). This innovative approach modifies a patient’s immune cells to better attack leukemia cells.
Additionally, allogeneic stem cell transplants have revolutionized treatment for many patients. This procedure involves transplanting stem cells from a compatible donor to help rebuild the patient’s immune system after chemotherapy (A Game Changer for Blood Cancer Treatment). Such advancements not only improve survival rates but also enhance the quality of life for those affected by leukemia.
In conclusion, understanding that leukemia originates in the bone marrow is essential for grasping the complexities of this disease. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, there is hope for improved outcomes for patients diagnosed with leukemia. For more information on support and resources available for those affected by leukemia, consider visiting organizations like Blood Cancer UK and Cancer Research UK.
Fact 2: There Are Four Main Types of Leukemia
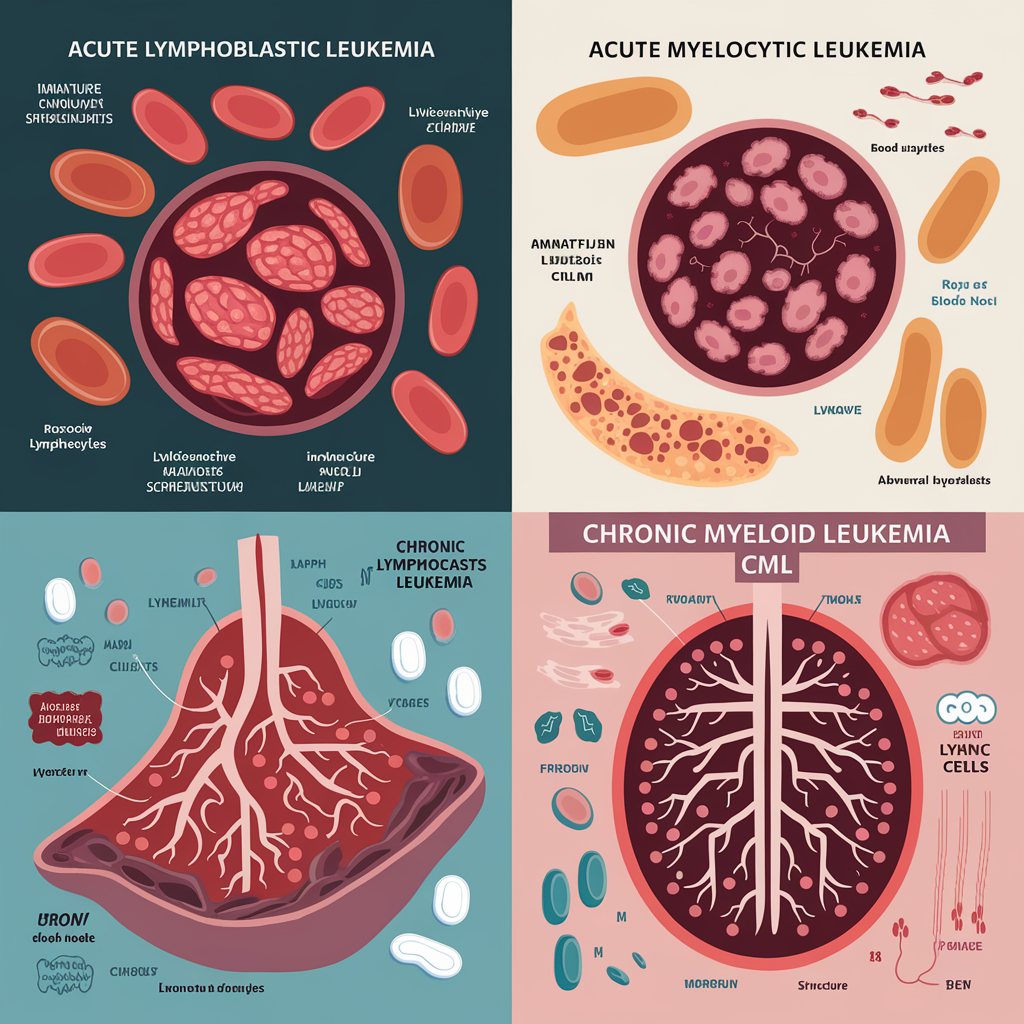
Leukemia is a complex cancer that primarily affects the blood and bone marrow. Understanding the different types of leukemia is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. The four main types of leukemia are:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): This type is most common in children but can also occur in adults. ALL progresses rapidly and requires immediate treatment. Symptoms often include fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bruising. Recent advancements in treatment, such as CAR T-cell therapy, have shown promise in improving outcomes for patients with ALL.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): AML is the most prevalent form of acute leukemia in adults. It can lead to a buildup of abnormal red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy, and researchers are exploring the potential of genomic sequencing to tailor therapies to individual patients. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) is actively funding research to enhance treatment strategies for AML, focusing on personalized medicine (Advances in Leukemia Research).
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): CLL is characterized by the slow accumulation of abnormal lymphocytes. It primarily affects older adults and may not require immediate treatment if symptoms are mild. However, when treatment is necessary, options include chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. Organizations like Blood Cancer UK provide resources and support for individuals coping with CLL.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): CML is marked by the overproduction of granulocytes in the bone marrow. The introduction of targeted therapies that inhibit the abnormal protein produced by the Philadelphia chromosome has significantly improved the prognosis for CML patients, allowing many to live near-normal life expectancies. The NCI highlights the importance of ongoing research in this area to further enhance treatment options (Leukaemia Counselling Service).
In summary, the four main types of leukemia—ALL, AML, CLL, and CML—each present unique challenges and treatment pathways. Ongoing research and advancements in therapies, including immunotherapy and targeted treatments, are crucial for improving patient outcomes. For more information on leukemia and support resources, visit Cancer Research UK and Leukaemia Care. Understanding these types can empower patients and families to make informed decisions about their care.
Fact 3: Leukemia Symptoms Can Be Subtle and Varied
Leukemia symptoms can often be subtle and varied, making early detection challenging. This type of cancer primarily affects the blood and bone marrow, leading to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. Understanding the symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
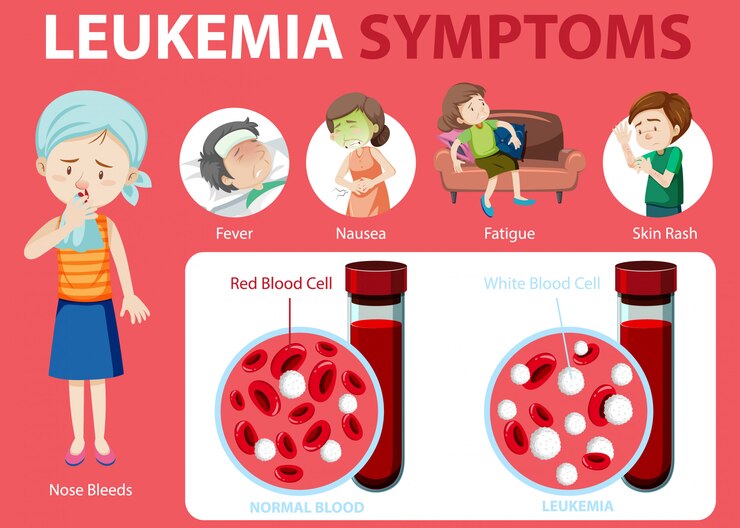
Common Symptoms of Leukemia
- Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms, fatigue in leukemia patients can be profound and persistent. This fatigue is often due to anemia, which occurs when the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to tissues.
- Frequent Infections: Individuals with leukemia may experience frequent infections due to the compromised immune system. The abnormal white blood cells produced in leukemia are often ineffective at fighting off infections, leading to increased susceptibility.
- Easy Bruising or Bleeding: Patients may notice unusual bruising or bleeding, such as frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums. This symptom arises from a low platelet count, which is essential for blood clotting.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a significant indicator of leukemia. This may occur due to the body’s increased energy expenditure in fighting the disease or due to a loss of appetite.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swelling in the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpits, or groin, can indicate leukemia. This swelling occurs as the body attempts to fight off the abnormal cells.
- Night Sweats: Many leukemia patients report experiencing night sweats, which can disrupt sleep and lead to further fatigue.
- Bone or Joint Pain: Pain in the bones or joints can occur as leukemia cells accumulate in the bone marrow, leading to discomfort and pain.
Types of Leukemia and Their Symptoms
Leukemia is categorized into several types, each with its own set of symptoms. For instance, Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) often presents with symptoms that develop rapidly, while Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) may have more gradual onset symptoms. Understanding these differences is vital for recognizing the disease early.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of leukemia can significantly improve treatment outcomes. The National Cancer Institute emphasizes the importance of recognizing these symptoms and seeking medical advice promptly. Advances in leukemia research, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies, have improved treatment options, making it essential for patients to be aware of their symptoms and seek help. For more information on leukemia research, visit the National Cancer Institute.
In conclusion, while leukemia symptoms can be subtle, being aware of them can lead to early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. For additional support and resources, organizations like Leukaemia Care and Blood Cancer UK offer valuable information and assistance.
Fact 4: Risk Factors for Leukemia Are Diverse
Leukemia is a complex disease with a variety of risk factors that can influence its development. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection. Here are some of the diverse risk factors associated with leukemia:
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic conditions can increase the risk of developing leukemia. For instance, individuals with Down syndrome or other genetic syndromes are at a higher risk. Research indicates that genetic mutations can lead to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells, a hallmark of leukemia. The National Cancer Institute highlights ongoing research into how these genetic factors contribute to leukemia’s onset.
- Environmental Exposures: Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene, has been linked to an increased risk of leukemia. Benzene is commonly found in industrial settings and is a known carcinogen. Additionally, exposure to radiation, particularly from previous cancer treatments, can elevate the risk of developing leukemia later in life.
- Age and Gender: Age is a significant risk factor, with leukemia being more common in older adults. However, certain types, like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), are more prevalent in children. Furthermore, men are generally at a higher risk than women for most types of leukemia, including Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
- Previous Cancer Treatments: Individuals who have undergone chemotherapy or radiation therapy for other cancers may have an increased risk of developing leukemia. This is particularly true for treatments involving alkylating agents, which can damage the DNA in healthy cells, leading to mutations that may result in leukemia.
- Immune System Disorders: People with weakened immune systems, whether due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or as a result of immunosuppressive therapy, are at a higher risk for leukemia. The immune system plays a critical role in identifying and eliminating abnormal cells, and its impairment can lead to the unchecked growth of these cells.
- Family History: A family history of leukemia can also be a risk factor. While most cases of leukemia occur sporadically, having a close relative with the disease can increase an individual’s risk, suggesting a potential genetic component.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for individuals and healthcare providers alike. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of leukemia, such as fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bruising, patients can seek timely medical advice. For more information on leukemia and its risk factors, consider visiting the Leukaemia Care website, which offers valuable resources and support for those affected by this disease.
Fact 5: Diagnosis Involves Multiple Tests
Diagnosing leukemia is a complex process that typically involves multiple tests to ensure an accurate assessment of the disease. This is crucial because leukemia, a type of cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow, can manifest in various forms, including Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Each type may require different diagnostic approaches and treatment plans.
Initial Evaluation
The diagnostic journey often begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Physicians will look for common symptoms of leukemia, such as fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising or bleeding, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms can overlap with other conditions, making it essential to conduct further tests for a definitive diagnosis.
Blood Tests
One of the first tests performed is a complete blood count (CBC). This test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In leukemia patients, the CBC often reveals an abnormal increase in white blood cells, which are typically immature and dysfunctional. For instance, in AML, the presence of myeloblasts can be indicative of the disease. Additionally, blood smears may be examined under a microscope to identify abnormal cells.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
If blood tests suggest leukemia, a bone marrow biopsy is usually the next step. This procedure involves extracting a small sample of bone marrow, typically from the hip bone, to analyze the presence of leukemia cells. The biopsy can provide critical information about the type of leukemia and its progression, guiding treatment decisions. According to the National Cancer Institute, advancements in genomic sequencing of tumor cells are also being explored to tailor treatment plans more effectively.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, may be employed to assess the extent of the disease and check for any organ involvement. These tests help determine if the leukemia has spread beyond the blood and bone marrow, which can significantly influence treatment options.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is becoming increasingly important in leukemia diagnosis. It helps identify specific mutations or chromosomal abnormalities, such as the Philadelphia chromosome in CML, which can inform targeted therapy options. The integration of targeted therapies and immunotherapies has revolutionized leukemia treatment, as highlighted in recent research from the Cancer Research UK.
Conclusion
In summary, diagnosing leukemia involves a multifaceted approach that includes blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, imaging studies, and genetic testing. Each of these components plays a vital role in accurately identifying the type of leukemia and determining the most effective treatment strategy. As research continues to advance, the hope is that these diagnostic methods will become even more precise, leading to better outcomes for patients. For more information on support services and resources, you can visit Leukaemia Care.
Fact 6: Treatment Options Are Advancing Rapidly
Advancements in the treatment of leukemia are occurring at an unprecedented pace, offering new hope to patients and their families. Leukemia, a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. The traditional treatment methods, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, have been the cornerstone of leukemia management for decades. However, recent developments in targeted therapies and immunotherapies are revolutionizing the landscape of leukemia treatment.
One of the most promising advancements is the use of targeted therapies, which focus on specific genetic mutations or abnormalities in leukemia cells. For instance, in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML), targeted therapies that inhibit the abnormal protein produced by the Philadelphia chromosome have significantly improved patient outcomes, allowing many individuals to achieve a near-normal life expectancy. This shift towards personalized medicine is crucial, as it tailors treatment to the unique genetic profile of each patient’s leukemia, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Moreover, immunotherapy is emerging as a powerful tool in the fight against leukemia. This approach harnesses the body’s immune system to combat cancer more effectively. Notably, CAR T-cell therapy has shown remarkable success, particularly in treating Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children and young adults. This innovative treatment involves modifying a patient’s own immune cells to better recognize and attack leukemia cells, leading to improved remission rates. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) is actively funding research to further explore these therapies, aiming to enhance treatment outcomes and reduce toxicity (Advances in Leukemia Research).
In addition to these therapies, allogeneic stem cell transplants are gaining traction as a viable treatment option. This procedure involves transplanting stem cells from a compatible donor to rebuild the patient’s immune system after intensive chemotherapy. Recent successes in this area, particularly at institutions like the University of New Mexico Comprehensive Cancer Center, highlight the potential of this approach to provide new avenues for patients with limited options (A Game Changer for Blood Cancer Treatment).
As treatment options for leukemia continue to evolve, it is essential for patients and their families to stay informed about the latest advancements. Support services, such as counseling and patient advocacy groups, play a vital role in helping individuals navigate their treatment journey. Organizations like Leukaemia Care and Blood Cancer UK provide valuable resources and support to those affected by leukemia, ensuring they have access to the information and assistance they need.
In conclusion, the rapid advancements in leukemia treatment options are transforming the prognosis for many patients. With ongoing research and innovation, the future looks promising for those battling this challenging disease. For anyone affected by leukemia, staying connected with healthcare providers and support networks is crucial to navigating the complexities of treatment and achieving the best possible outcomes.
Fact 7: Leukemia Treatment Side Effects Can Be Managed
Managing the side effects of leukemia treatment is a crucial aspect of patient care that can significantly enhance the quality of life for those undergoing therapy. Leukemia, a type of cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow, often requires aggressive treatment methods such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplants. While these treatments are essential for combating the disease, they can also lead to a range of side effects that may be challenging for patients to navigate.
Recent advancements in leukemia treatment have introduced targeted therapies and immunotherapies, which aim to reduce the toxicity associated with traditional methods. For instance, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) has highlighted the potential of CAR T-cell therapy and bispecific T-cell engagers in treating various forms of leukemia, particularly in children and young adults. These innovative approaches not only target cancer cells more effectively but also minimize damage to healthy cells, thereby reducing side effects. You can learn more about these advancements in the NCI’s research on leukemia.
In addition to medical advancements, support services play a vital role in managing the emotional and psychological impacts of leukemia treatment. Organizations like Leukaemia Care offer counseling services that help patients and their families cope with the stress and anxiety that often accompany a leukemia diagnosis. These resources are essential for fostering resilience and providing emotional support during treatment.
Moreover, understanding the specific side effects associated with different types of leukemia treatments can empower patients to take proactive steps in managing their health. Common side effects include fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bruising or bleeding. Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about any side effects they experience, as this can lead to timely interventions and adjustments in treatment plans.
Financial support is also available for those affected by leukemia, which can alleviate some of the burdens associated with treatment. Organizations like Blood Cancer UK provide information on benefits and legal protections against workplace discrimination, ensuring that patients receive the support they need during their treatment journey.
In conclusion, while leukemia treatment can lead to significant side effects, advancements in therapy and robust support systems are available to help manage these challenges. By leveraging these resources, patients can navigate their treatment more effectively, improving their overall well-being and quality of life. For more information on living with leukemia and accessing support, consider reaching out to organizations dedicated to blood cancer care.
Fact 8: Leukemia Survival Rates Are Improving
Leukemia survival rates have seen significant improvements over the past few decades, thanks to advancements in research and treatment options. Leukemia, a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. The main types include Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML), and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Each type presents unique challenges, but ongoing research is paving the way for better outcomes.
Recent studies funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) highlight the progress made in both targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These innovative treatments are designed to be more effective and less toxic than traditional methods like chemotherapy and radiation therapy. For instance, CAR T-cell therapy, which involves genetically modifying a patient’s immune cells to attack cancer, has shown promising results, particularly in children and young adults with ALL.
Moreover, the introduction of targeted therapies has transformed the treatment landscape for CML. These therapies specifically block the abnormal proteins produced by the Philadelphia chromosome, leading to a near-normal life expectancy for many patients. This is a remarkable shift from the past, where treatment options were limited and often less effective.
The survival rates for leukemia patients have improved significantly due to these advancements. For example, the five-year survival rate for ALL has increased from around 50% in the 1970s to over 90% today, reflecting the impact of modern treatment strategies. Similarly, AML patients now have access to more personalized treatment plans, thanks to genomic sequencing that helps doctors tailor therapies to individual needs.
Support services also play a crucial role in improving outcomes for leukemia patients. Organizations like Leukaemia Care provide essential resources and counseling to help patients and their families cope with the emotional and psychological impacts of the disease. These support networks are vital for navigating the complexities of treatment and recovery.
In conclusion, the landscape of leukemia treatment is evolving rapidly, with research and innovation leading to improved survival rates. As therapies become more targeted and personalized, the outlook for patients continues to brighten. For those affected by leukemia, staying informed about the latest advancements and accessing support services can make a significant difference in their journey. For more information on living with leukemia, visit Blood Cancer UK for resources and support.
Fact 9: Living with Leukemia Requires Comprehensive Care
Living with leukemia requires a comprehensive approach to care that addresses not only the physical aspects of the disease but also the emotional and psychological challenges faced by patients and their families. Leukemia, a type of cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow, is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. The complexity of this disease necessitates a multifaceted treatment strategy that includes traditional therapies, innovative treatments, and robust support systems.
Treatment Options
The treatment landscape for leukemia has evolved significantly over the years. Traditional methods such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy remain foundational, but advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have transformed patient outcomes. For instance, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) highlights the potential of CAR T-cell therapy and bispecific T-cell engagers, particularly for children and young adults with leukemia (Advances in Leukemia Research). These therapies harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively, offering hope where conventional treatments may fall short.
Moreover, the introduction of allogeneic stem cell transplants has marked a significant milestone in leukemia care. This procedure involves transplanting stem cells from a compatible donor to rebuild the patient’s immune system after chemotherapy, providing a new avenue for treatment (A Game Changer for Blood Cancer Treatment). Such advancements not only improve survival rates but also enhance the quality of life for patients.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with leukemia can be emotionally taxing. Patients often experience anxiety, depression, and uncertainty about their future. Therefore, access to support services is crucial. Organizations like Leukaemia Care provide counseling services that help patients and their families cope with the emotional impacts of the disease. These services are essential for fostering resilience and providing a safe space for patients to express their feelings and concerns.
Financial and Legal Considerations
Financial support is another critical aspect of comprehensive care. Patients may face significant medical expenses, and understanding their rights at work is vital. Resources such as Blood Cancer UK offer guidance on available financial assistance and legal protections against workplace discrimination. This support ensures that individuals with leukemia can focus on their treatment without the added stress of financial burdens.
Conclusion
In summary, living with leukemia necessitates a comprehensive care approach that integrates medical treatment, emotional support, and financial guidance. By leveraging advancements in treatment and accessing available resources, patients can navigate their journey with greater confidence and hope. For more information on living with leukemia and available support, consider reaching out to organizations like Cancer Research UK and Leukaemia Care.
Fact 10: Leukemia Research Continues to Break New Ground
Leukemia research is making significant strides, offering hope to patients and their families. This type of cancer, which affects the blood and bone marrow, is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) is at the forefront of this research, funding studies aimed at improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects. Recent advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies are transforming the landscape of leukemia treatment, making it more effective and less toxic than traditional methods like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
One of the most promising developments in leukemia treatment is the use of CAR T-cell therapy. This innovative approach involves genetically modifying a patient’s own immune cells to better recognize and attack leukemia cells. Research indicates that this therapy has shown remarkable success, particularly in treating Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children and young adults. The potential of CAR T-cell therapy is a testament to the progress being made in the field of leukemia research, as highlighted in the Advances in Leukemia Research.
Additionally, bispecific T-cell engagers are being explored as a new treatment option. These agents can simultaneously bind to T-cells and leukemia cells, enhancing the immune response against the cancer. This dual-targeting strategy is part of a broader trend towards personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient’s disease.
For adults, Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) has seen a dramatic improvement in prognosis due to targeted therapies that inhibit the abnormal protein produced by the Philadelphia chromosome. Patients with CML now have a life expectancy close to normal, thanks to these advancements. The NCI continues to support research that aims to refine these therapies further, ensuring that they are accessible to all patients.
Moreover, the introduction of allogeneic stem cell transplants has opened new avenues for treating various blood cancers, including leukemia. This procedure involves transplanting stem cells from a compatible donor, which can help rebuild the patient’s immune system after chemotherapy. The University of New Mexico Comprehensive Cancer Center has recently pioneered this approach, marking a significant milestone in blood cancer treatment.
As research continues to evolve, the importance of support services cannot be overstated. Organizations like Leukaemia Care provide essential counseling and resources for patients and their families, helping them navigate the emotional and psychological challenges of a leukemia diagnosis. Furthermore, resources from Blood Cancer UK offer vital information on financial support and workplace rights for those affected by blood cancer.
In conclusion, the landscape of leukemia treatment is rapidly changing, with ongoing research paving the way for more effective and personalized therapies. As we continue to learn more about this complex disease, the hope for improved outcomes grows stronger. For those affected by leukemia, staying informed about the latest advancements and available support is crucial. Engaging with healthcare professionals and support organizations can provide invaluable assistance in managing this challenging condition.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with Knowledge About Leukemia
Understanding leukemia is crucial for empowering yourself and others affected by this complex disease. As a type of cancer that impacts the blood and bone marrow, leukemia is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. There are several types of leukemia, including Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Each type presents unique challenges and treatment options, making it essential to stay informed about the latest advancements in research and therapy.
Recent studies funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) have made significant strides in understanding how to treat leukemia more effectively. Traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy are now complemented by innovative approaches like targeted therapies and immunotherapies. For instance, CAR T-cell therapy has shown promise in treating various forms of leukemia, particularly in children and young adults. This therapy involves modifying a patient’s immune cells to better fight cancer, showcasing the potential of personalized medicine in improving treatment outcomes.
Moreover, support services play a vital role in the journey of those diagnosed with leukemia. Organizations like Leukaemia Care offer counseling services that help patients and their families cope with the emotional and psychological impacts of the disease. Accessing these resources can provide much-needed support during challenging times.
In addition to emotional support, understanding your rights and available resources is essential. The Blood Cancer UK website provides information on financial assistance and legal protections for individuals diagnosed with blood cancer, ensuring that they receive the support they need in the workplace and beyond.
As research continues to evolve, the introduction of allogeneic stem cell transplants has marked a significant milestone in the treatment of blood cancers, including leukemia. This innovative approach not only enhances treatment accessibility but also addresses the challenges of donor matching, particularly in diverse populations (University of New Mexico Comprehensive Cancer Center).
In conclusion, empowering yourself with knowledge about leukemia involves understanding the disease, exploring treatment options, and accessing support services. By staying informed and connected with resources, you can navigate the complexities of leukemia more effectively. For more information, consider reaching out to organizations like Cancer Research UK or utilizing platforms like Medistine for online medical consultations and second opinions. Your journey through leukemia can be supported by knowledge, community, and the latest advancements in research.